Nutrition in Recovery: Creating Balanced Meals for Optimal Healing

Table of Contents Seeking Drug Or Alcohol Detox? Sullivan Recovery is a leading drug and alcohol detox in Mission Viejo, California. Call Today! Clinically Reviewed By: Rachel Sweet | LMFT Nutrition in Recovery: Creating Balanced Meals for Optimal Healing Introduction Nutrition in Recovery plays a pivotal role in the recovery process from substance use disorders. A nutritious diet helps repair the body, improve brain function, and stabilize emotional well-being. For individuals in recovery, proper dietary choices support both physical health and mental clarity throughout the recovery journey. Significance of Nutrition in Recovery Proper nutrition is essential for the healing process. A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients helps the body perform necessary bodily functions, including hormone production, neurotransmitter function, and energy production. A focus on healthy eating habits also reduces cravings for drugs and improves emotional stability. Impact of Substance Abuse on Nutritional Health Substance abuse often leads to a poor diet, nutrient deficiencies, and nutritional imbalances. Many addictive substances interfere with nutrient absorption, disrupt the digestive process, and damage organs like the liver and stomach lining. Over time, this can cause electrolyte imbalances, Vitamin deficiencies, and deficiencies of vitamins and essential minerals like folic acid, vitamin B6, and trace minerals. People with alcohol addiction or drug addiction may experience weight loss, poor concentration, mood swings, and cravings for substances due to lack of adequate nutrition and nutrient-rich foods. Role of Nutrition in Physical Recovery Repairing Physical Damage A diet rich in lean proteins, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats like olive oil supports tissue repair, organ function, and overall body repair. It also helps reverse the effects of organ damage caused by chronic drug or alcohol abuse. Detoxification and Withdrawal Management The detoxification process places high demand on the body. Eating nutrient-dense foods helps support the detoxification processes and manage withdrawal symptoms. Key nutrients like amino acids, complex carbohydrates, and cruciferous vegetables help combat oxidative stress and regulate electrolyte balance and fluid balance. Addressing Nutritional Deficiencies Nutritional deficiencies are common in people with a history of addiction to drugs or alcohol. Replenishing vital nutrients like essential vitamins, amino acids, and Omega-3 fatty acids supports nerve function, neurotransmitter production, and cognitive function. Impact on Mental and Emotional Well-being Balancing Brain Chemistry Nutrition affects dopamine levels, serotonin, and other neurotransmitters. A nutrient-rich diet with foods rich in amino acids, Omega-3 fatty acids, and essential substances supports healthy brain chemistry, easing symptoms like brain fog, mood disorders, and cognitive impairments. Stabilizing Mood and Energy Levels Balanced meals help regulate blood sugar levels and maintain steady energy levels. This reduces emotional eating, mood swings, and helps stabilize energy levels stable throughout the day. Reducing Cravings Low blood sugar or poor nutrition can increase cravings for drugs or alcohol. Eating regular meals and maintaining a balanced intake of protein-rich foods, leafy greens, and healthy fats reduces the desire for food that’s triggered by emotional or physical stress. Enhancing Overall Mental Health Good nutrition improves mental health, mental well-being, and supports those with mental health disorders or co-occurring disorders. A comprehensive approach that includes nutrition therapy can reduce symptoms like anxiety, depression, and poor concentration. Essential Dietary Guidelines for Recovery Prioritizing Whole, Nutrient-Dense Foods Choose a well-balanced diet filled with nutrient-dense foods like leafy vegetables, citrus fruits, fresh produce, dairy products, and whole grains. These provide a wide range of vital nutrients to support both the mind and body during recovery. Importance of Staying Hydrated Drink plenty of water—at least 8 glasses of water or cups per day. Staying hydrated improves metabolic rate, nutrient absorption, and supports the body’s detoxification processes. Use of Supplements for Specific Deficiencies In cases of common deficiencies, nutritional supplements like mineral supplements, vitamin B6, folic acid, or Omega-3 fatty acids may be needed. Always consult a healthcare provider or registered dietitian to determine appropriate dietary interventions. Incorporating Nutrition in Recovery Plans Nutritional Education Educational programs can provide dietary recommendations, improve understanding of adequate intake, and help individuals adopt dietary approaches that support long-term recovery. Meal Planning Personalized meal plans support healthy lifestyle choices and help avoid unhealthy foods. Planning meals per day ensures consistent carbohydrate intake and supports stable energy levels. Professional Guidance from a Registered Dietitian Nutritionist Registered dietitians help design nutritional plans that meet individual needs. They address common challenges like emotional challenges, Gastrointestinal Disorders, and weight gain during recovery. Addressing Co-occurring Conditions People in addiction treatment programs often have co-occurring disorders. A holistic approach that includes nutrition therapy helps support mental health and reduce relapse risk. Establishing Healthy Eating Habits Mindful Eating Practices Mindful eating helps people notice feelings of hunger and fullness, improving dietary habits and reducing the risk of emotional eating. Building Self-esteem and Improving Body Image Eating a healthy diet improves physical and mental well-being, supporting body repair and a more positive body image. This can boost self-esteem and promote a sober lifestyle. Creating Sustainable Eating Habits Developing healthy eating routines with a variety of foods supports sustained recovery. A consistent diet during recovery also helps regulate blood pressure, enhance immune function, and protect against chronic diseases like heart disease or liver disease. Seeking Treatment? We Can Help! At Sullivan Recovery, as an in-network provider we work with most insurance plans, such as: Tricare Blue Shield Magellan Health First Health Network The Holman Group Cigna Anthem BCBS Aetna Humana TriWest HMC Healthworks Molina UnitedHealthcare Optum UMR And More If you or a loved one are struggling with mental health challenges or substance abuse, reach out to Sullivan Recovery today. Our team of compassionate professionals is here to support your journey towards lasting well-being. Give us a call at 949-836-7180. Frequently Asked Questions 1. Why is nutrition important during addiction recovery? Nutrition plays a vital role in supporting both physical healing and mental well-being during recovery. Substance use often leads to nutritional deficiencies, which can affect brain function, immune function, and energy levels. Eating a balanced diet filled with nutrient-rich foods helps the body recover, stabilizes mood, and reduces cravings for substances. 2. What are the best foods to
Life After Rehab: What to Expect and How to Stay on Track

Table of Contents Seeking Drug Or Alcohol Detox? Sullivan Recovery is a leading drug and alcohol detox in Mission Viejo, California. Call Today! Clinically Reviewed By: Rachel Sweet | LMFT Life After Rehab: What to Expect and How to Stay on Track Life after rehab can feel like starting over. At Sullivan Recovery, we help individuals create a sober life rooted in structure, support, and purpose. This guide explores how people in recovery can manage everyday life, avoid the risk of relapse, and build a foundation for long-term recovery. The Journey of Adjustment Life in recovery begins with change. Leaving a rehab facility means returning to the real world, where triggers and stress can resurface. The recovery process is a lifelong process, not a quick fix. Adjusting takes patience, structure, and the right recovery tools. Managing Expectations It’s important to keep expectations realistic. Individuals in recovery may face emotional challenges, shifting social circles, or changes in relationships with family. Successful recovery is not perfect—it’s consistent effort backed by a solid treatment plan and a commitment to recovery. Navigating New Lifestyles Sober living programs support the shift from active addiction to a stable, sober life. Changing routines, avoiding triggers, and finding healthy activities are all part of the new normal. Establishing a new social circle can strengthen your path to recovery. The Importance of Continuing Care Ongoing recovery depends on aftercare services and long-term support. Treatment centers often recommend participation in aftercare programs as part of a comprehensive aftercare plan. Individual Therapy Individual therapy helps address underlying issues like trauma, anxiety, or mental health issues. These evidence-based therapies play a key role in the recovery journey. Support Groups and Meetings Joining 12-step program support groups like Alcoholics Anonymous, Narcotics Anonymous, or Cocaine Anonymous offers structure and peer support. These 12-step meetings help reduce the relapse rate by keeping you connected and accountable. Sober Living Arrangements Sober living homes, also known as transitional living homes, provide a structured environment for those stepping out of a rehab program. These community living setups allow for daily life to be managed without the pressure of outside triggers. Recovery housing is especially helpful for those without a stable home environment. Recognizing and Managing Personal Triggers Recovery from addiction involves learning how to spot triggers early and deal with them before they lead to relapse. Identifying Triggers Triggers can stem from stress, people, or memories tied to substance abuse or alcohol addiction. Keeping a journal can help track what increases cravings for drugs or alcohol. Developing Coping Strategies Healthy coping means replacing old habits with new ones. People in recovery can manage stress through physical activity, dance lessons, or time with supportive individuals. These strategies build a solid foundation for lifelong recovery. Building a Strong Support Network A supportive community can make the difference between relapse and recovery. Role of Family and Friends Family therapy helps rebuild relationships with people close to you. It also teaches healthy boundaries and clear roles in the treatment process. Finding Community Support Supportive individuals may include alumni from your rehabilitation program, neighbors, or church members. Many alumni programs offer social events, fun activities, and regular check-ins to support long-term sobriety. Communication Strategies Good communication helps prevent conflict and rebuild trust. Honest and Open Conversations Use simple, honest language when discussing your addiction recovery. Share how others can support your ongoing therapy or aftercare plan. Handling Difficult Discussions Tough conversations are part of healing. Discuss boundaries, feelings, and expectations clearly. This promotes healthier relationships and reduces tension in your daily life. Engaging in Healthy Lifestyle Practices A healthy lifestyle supports your physical and mental well-being. Nutrition and Exercise Fuel your body with healthy foods and stay active. These habits improve physical health and reduce anxiety. Good health helps manage chronic health condition risks tied to substance use disorders. Mental Health and Mindfulness Use mindfulness, meditation, or breathing exercises to reduce stress. Address any behavioral health conditions with your health care provider or treatment team. Embracing New Hobbies Hobbies like painting, hiking, or volunteering keep your mind busy and away from old habits. Try sober activities that bring joy and purpose. Understanding and Utilizing Aftercare Programs A strong aftercare program can prevent relapse and promote independence. 12-Step Support Groups 12-step groups like Alcoholics Anonymous or 12-step fellowship meetings are widely available. Use the online treatment locator or ask your treatment provider for suggestions. Therapy and Counseling Options Continue with individual counseling, group therapy, or counseling sessions. Consistent care helps you stay on track with your recovery goals. Rebuilding Relationships Restoring trust is a slow but necessary part of life after addiction. Restoring Trust Be honest and consistent. Show loved ones they can depend on you again. Actions matter more than words. Setting Boundaries Protect your life of sobriety by limiting contact with people who promote alcohol abuse or drug abuse. Clear boundaries are part of successful recovery. Prioritizing Self-Care Taking care of yourself is not selfish—it’s survival. Daily Routines for Well-being Plan your day. Include time for rest, work, and positive habits. Use tools like accountability check-ins or an accountability partner for structure. Stress Management Techniques Use coping skills like journaling, yoga, or spending time in nature. Avoid burnout. Watch for signs of relapse like isolation, irritability, or skipping regular meetings. Staying Vigilant Against Relapse Recovery is fragile. Stay alert. Recognizing Warning Signs Monitor your thoughts, behaviors, and moods. Stay connected with your treatment provider and supportive community. Seeking Help Quickly If you slip or feel overwhelmed, reach out. Call your therapist, sponsor, or an addiction specialist. Immediate help can prevent a full relapse. Conclusion: Embracing a Sober Life Life after treatment is filled with growth, change, and opportunity. With a treatment facility, aftercare planning, and strong community support, people in recovery can reclaim a quality of life that addiction once took away. Stay committed. Stay connected. Embrace your life on life—one day at a time. Seeking Treatment? We Can Help! At Sullivan Recovery, as an in-network provider we work with most insurance
Understanding the Cycle of Addiction

Table of Contents Seeking Drug Or Alcohol Detox? Sullivan Recovery is a leading drug and alcohol detox in Mission Viejo, California. Call Today! Clinically Reviewed By: Rachel Sweet | LMFT Understanding the Cycle of Addiction The cycle of addiction describes how substance use can evolve into a chronic condition known as substance use disorder. This disorder involves compulsive drug-seeking behaviors despite harmful consequences. At Rize OC, our mission is helping people break this addiction cycle through professional treatment and comprehensive support. Stages of Addiction Recognizing the stages of addiction helps individuals understand how casual use can progress into severe substance dependence. Experimentation Stage The addiction cycle starts with the experimentation stage. During this period of time, individuals first try an addictive substance, often due to peer pressure or curiosity. Initial experiences involve pleasurable feelings from the release of dopamine, reinforcing continued substance use. Regular Use Stage After experimentation, some people progress to regular substance use. The substance of choice becomes part of daily life or social settings. While usage seems controlled, regular use can quickly lead to bad habits and addictive behaviors. Misuse and Abuse Stage The abuse stage involves heavy substance misuse, including alcohol abuse and drug abuse. At this stage of addiction, harmful consequences begin to appear, such as health problems, legal consequences, and impaired daily functioning. Tolerance Development Stage Tolerance development occurs when individuals require greater amounts of the addictive substance to achieve the desired pleasurable feelings. This increases addiction risk, as tolerance leads directly to chronic misuse of prescription drugs, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Dependence Stage Dependence marks a critical addiction stage involving both physical dependence and psychological dependence. Physical dependence causes withdrawal symptoms like nausea, shaking, or other physical symptoms if drug use stops. Psychological dependence results in severe cravings, anxiety, or negative feelings without the substance. Addiction Stage Full-blown addiction involves compulsive substance use despite severe adverse consequences. The addicted individual experiences intense cravings and struggles to control drug-seeking behaviors. At this point, addiction is a chronic brain disease significantly affecting brain chemistry and normal functioning. Relapse Stage Relapse often occurs during recovery and involves returning to addictive behaviors after extended periods of abstinence. Stress-induced relapse or physical relapse is common due to the activation of stress neurotransmitters or encountering triggers. High relapse rates highlight the importance of effective aftercare in the recovery program. Understanding Key Concepts Physical Dependence vs. Psychological Dependence Physical dependence occurs when the body needs the substance to function normally. Withdrawal symptoms become common when substance use stops. Common physical effects include shaking, sweating, and nausea. Psychological dependence involves emotional reliance on drugs or alcohol. Individuals experience severe cravings and negative feelings without the substance, driving compulsive drug-seeking behavior. Risk Factors for Addiction The development of addiction involves several key risk factors: Genetic factors and family history of addiction Presence of mental health disorders, including post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety, and depression Environmental factors such as social settings and peer pressure Early adverse childhood experiences increasing susceptibility to addiction Misuse of prescription medications or illicit drugs These risk factors contribute significantly to an individual’s vulnerability to substance use. Signs and Symptoms of Addiction Common signs of addiction include: Continued substance use despite negative consequences Compulsive drug seeking or risky behavior Increased tolerance and physical dependence Isolation from friends and family Legal and financial problems Neglecting physical health and emotional health Withdrawal symptoms without substance use Identifying these symptoms early is critical for successful intervention. The Recovery Process The recovery process requires understanding of substance use disorder and structured professional treatment. Effective treatment breaks the vicious cycle of addiction. Recognizing the Need for Change Recovery begins when the addicted person recognizes the need for change. Acknowledging harmful consequences and the chronic disease nature of addiction motivates individuals to seek help. Treatment Options Professional treatment at an addiction treatment center like Rize OC includes: Medical detox (drug detox) to manage physical dependence safely Individual behavioral therapies addressing psychological factors Family therapy to rebuild relationships and address family dynamics Medication-assisted treatment for severe substance dependence, such as opioid addiction or alcohol addiction Education about mental health issues and co-occurring mental health disorders Professional treatment improves the likelihood of long-term recovery. Aftercare Strategies Aftercare strategies reduce the risk of relapse by supporting individuals after primary treatment. These include: Participation in Alcoholics Anonymous or similar support groups Continued behavioral therapies to manage compulsive drug seeking Developing healthy habits and coping strategies for stress Regular monitoring of mental health conditions and emotional health Building a strong support network through family, peers, or counselors Effective aftercare strengthens the path to recovery. Breaking the Cycle of Addiction Breaking the addiction cycle requires addressing both physical and psychological aspects of addiction. Self-Help and Support Groups Self-help groups like Alcoholics Anonymous offer valuable peer support. Individuals share personal experiences, providing encouragement and strategies for managing daily life without addictive drugs or alcohol. Building a Support Network Creating a strong support network is crucial. Support systems typically include: Family and friends educated about substance abuse Professional counselors or therapists Peers in recovery sharing similar individual experiences Strong support networks reduce relapse risk by providing emotional and practical assistance. The Science Behind Addiction Research from organizations such as the Mental Health Services Administration and American Psychiatric Association identifies addiction as a chronic brain disease. Brain imaging studies published in the American Journal of Psychiatry and Behavioural Brain Research highlight changes in brain chemistry due to addictive substances. These changes affect dopamine levels, serotonin neurotransmitter function, and overall human brain activity, reinforcing compulsive substance use and repetitive behaviors. Additionally, the Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment emphasizes individual differences and gender differences in addiction vulnerability, further supported by Behavioral Health Statistics. Understanding these key characteristics guides personalized addiction treatment. How Rize OC Can Help At Rize OC, we recognize addiction as a medical condition requiring comprehensive, professional treatment. Our evidence-based programs address drug use disorder, alcohol dependence, and co-occurring mental health disorders. Our trained professionals assist clients in managing the physical effects of
Siblings of Addicts: Coping, Boundaries, and Support

Table of Contents Seeking Drug Or Alcohol Detox? Sullivan Recovery is a leading drug and alcohol detox in Mission Viejo, California. Call Today! Clinically Reviewed By: Rachel Sweet | LMFT Siblings of Addicts: Coping, Boundaries, and Support Siblings of addicts experience a unique set of challenges within their family unit. Addiction is a family disease, significantly affecting the entire family. Understanding substance use disorder and how it impacts siblings of addicts can help families heal together and support their loved one’s journey to recovery. Understanding Addiction Definition of Addiction Addiction, also known as substance use disorder, is a brain disease characterized by compulsive substance abuse despite negative consequences. Individuals with substance use disorders struggle with drug addiction, alcohol addiction, or other problematic substance use, making it difficult to maintain healthy family dynamics. Common Types of Addiction Common addictions affecting families include: Drug abuse (opioids, stimulants) Alcohol use disorder Behavioral addictions Addiction within families is often influenced by genetic predisposition and difficult family life experiences. The Emotional Impact on Siblings The devastating impact of addiction significantly affects siblings of individuals struggling with addiction. Adult siblings and younger family members often suffer emotional distress and strained relationships. Conflicting Feelings: Love vs. Resentment Siblings of addicts may experience conflicting emotions. They feel love and empathy towards family members struggling with addiction but also resentment due to ongoing family issues and the attention given to their addicted sibling. Guilt and Enabling Behaviors The experience of siblings may involve feelings of guilt, leading non-addicted siblings to adopt a caretaker role. This can unintentionally enable substance abuse behaviors, reinforcing their sibling’s addiction issue rather than supporting recovery. Isolation and Misunderstanding Siblings often feel isolated and misunderstood, especially if their family situation involves dysfunction. Mental health issues and loss of illusions about a normal family life can leave siblings feeling alone. Effects on Family Dynamics Addiction alters family roles and family systems, resulting in dysfunctional family dynamics. Family ties become strained, affecting the mental health of the individual family members. Sibling-Sibling Relationships Sibling relationships suffer when dealing with an addicted sibling. Strained relationships become common, especially if siblings witness the devastating impact of drug addiction or alcohol use disorder firsthand. Parent-Sibling Relationships Parental attention often shifts entirely to the addicted child, creating tension and resentment among siblings. Financial strain, poor hygiene, or unpredictable behaviors associated with addiction further disrupt family dynamics. Family Roles and Responsibilities Family roles shift significantly in families affected by addiction. Siblings may assume roles like the caretaker role, family clown, or protector to cope with their difficult family life. Such roles add pressure and disrupt normal sibling relationships. Setting Healthy Boundaries Healthy boundaries are essential for siblings of addicts to protect their mental health and support the recovery process of their addicted family members. Importance of Boundaries Boundaries help siblings maintain emotional health, prevent enabling behaviors, and minimize the negative impact of addiction on their lives. How to Set Boundaries Effectively Siblings of addicts can set boundaries effectively by: Clearly defining acceptable behaviors. Limiting interactions involving substance abuse. Maintaining consistent communication about personal limits. Communicating Boundaries to Family Members Open and honest communication about boundaries can reduce conflict and clarify expectations within the family unit. Family therapy sessions guided by mental health professionals can support this process. Self-Care for Siblings Self-care is crucial for siblings coping with addiction within families. Recognizing the need for personal support and implementing strategies to manage mental health issues is vital. Recognizing the Need for Self-Care Non-addicted siblings must acknowledge when addiction’s impact affects their mental health and daily life. Adult mental health should be a priority to manage emotional stress effectively. Strategies for Maintaining Mental Health Effective self-care strategies include: Engaging in individual therapy or family therapy. Attending a Family Support Group or sibling-focused support groups. Participating in relaxing activities and maintaining healthy routines. Seeking Support from Others Support from friends, family, and professional counseling can reduce isolation. Mental health professionals, family therapists, and intervention teams provide essential resources to siblings of addicts. Supporting a Struggling Sibling Siblings play a crucial role in the addicted individual’s recovery process. Offering support through education and open communication can positively influence the sibling with addiction. Educating Oneself about Addiction Understanding addiction as a brain disease helps siblings develop empathy towards family members and reduces stigma. Educational materials from reputable sources like the Journal of Loss and Trauma or Child Development journals can be valuable. The Role of Open Communication Honest dialogue allows siblings to address addiction issues directly without causing additional strain. Techniques such as thematic analysis and dialogical narrative analysis from qualitative studies highlight the effectiveness of clear communication. Encouraging Treatment Options Encouraging addiction treatment is an important step siblings can take. Sharing quality treatment resources, discussing available forms of treatment, and connecting with a treatment facility’s admissions team or intervention team can motivate the addicted sibling toward professional help. Resources for Siblings Several resources support siblings coping with addiction’s devastating impact. Support Groups and Communities Family Support Groups and online communities specifically for siblings of addicts provide valuable emotional support. Siblings can share focused summary stories or sibling stories to connect with others experiencing similar challenges. Educational Materials and Literature Educational resources like current studies, books, or articles provide insights into the effects of addiction on family members. Professional literature addressing the co-sibling experience or bereaved siblings piece offers important perspectives. Professional Help and Counseling Options Professional counseling and family therapy sessions assist in managing dysfunctional family dynamics. Treatment facilities like North Jersey Recovery Center offer family-focused addiction treatment options and comprehensive substance use services. Conclusion Siblings of addicts face unique challenges within their family unit. Understanding the negative impact of addiction, establishing healthy boundaries, prioritizing self-care, and seeking professional support empowers siblings to cope effectively. By actively participating in the family’s recovery process, siblings contribute positively to their loved one’s journey toward lasting recovery. Seeking Treatment? We Can Help! At Sullivan Recovery, as an in-network provider we work with most insurance plans, such as: Tricare Blue Shield
Relationships in Recovery: Building Strong Connections for Lasting Sobriety

Table of Contents Seeking Drug Or Alcohol Detox? Sullivan Recovery is a leading drug and alcohol detox in Mission Viejo, California. Call Today! Clinically Reviewed By: Rachel Sweet | LMFT Relationships in Recovery: Building Strong Connections for Lasting Sobriety The Importance of Relationships in Recovery The recovery journey is not just about quitting an addictive substance; it’s about rebuilding meaningful relationships that support a life of sobriety. The nature of addiction often strains personal relationships, leading to damaged relationships and broken trust. Developing healthier relationships during the recovery process plays a crucial role in maintaining sobriety. A person in recovery needs supportive relationships that encourage personal growth, emotional stability, and healthy boundaries to avoid the risk of relapse. Types of Relationships in Recovery Relationships in recovery can take many forms, including: Family relationships – Addiction is a family disease, and relationships with family often require healing after substance misuse. Building trust and fostering healthy communication can repair a broken relationship. Romantic relationships – An intimate relationship can provide support, but an unhealthy relationship may cause relationship stress and increase the risk of relapse. Friendships and social circles – Developing healthier connections helps individuals maintain sobriety while avoiding situations with drugs. Professional relationships – Therapists, addiction recovery experts, and treatment providers guide the healing process and help develop a relapse prevention plan. 12-step support groups – Engaging in 12-step meetings or 12-step and non-12-step groups provides accountability and emotional reinforcement. Healthy Relationships A healthy relationship in recovery is based on mutual respect, honest communication, and personal accountability. Characteristics of healthy relationships include: Healthy communication that fosters positive interactions Respect for personal boundaries and individual journey Encouragement for sobriety goals and positive coping skills Support during difficult times without enabling addictive behaviors Unhealthy Relationships Toxic relationships can threaten addiction recovery efforts. Signs of an unhealthy relationship include: Lack of respect or lack of communication Codependent relationship dynamics that prevent mutual growth Toxic behavior such as manipulation, physical abuse, or emotional highs followed by negative self-talk Encouraging substance misuse or engaging in unhealthy coping mechanisms The Impact of Healthy Relationships on Recovery Emotional Support and Well-being Supportive relationships provide a safe space for emotional health and mental health issues. People who have a strong relationship with healthy people are less likely to feel isolated during the stages of recovery. Enhanced Communication Skills Developing communication skills helps a person in recovery rebuild interpersonal relationships and strengthen social interactions. Active listening fosters healthy connections and prevents communication breakdowns. Increased Accountability Accountability in recovery can help individuals stay focused on sobriety goals. Engaging in a recovery program, like a 12-step program, strengthens personal accountability and relationship choices. The Dangers of Unhealthy Relationships in Recovery Understanding Codependency Codependent people often develop a dysfunctional relationship where they prioritize the needs of others over their own recovery process. This can lead to addictive patterns and unhealthy behaviors. Identifying Toxic Behavior Patterns Recognizing toxic behavior such as control, guilt-tripping, or abusive behavior is essential for maintaining beneficial relationships in recovery. The Risk of Relapse An addicted person in an unhealthy relationship may face an increased risk of relapse due to emotional distress and exposure to substance addiction. Key Skills for Navigating Relationships in Recovery Setting Boundaries Healthy boundaries protect against relationship stress and toxic people. Boundaries help a person in recovery maintain emotional connections without sacrificing their recovery journey. Effective Communication Strategies Good communication skills promote honest communication, preventing relationship issues and misunderstandings. Prioritizing Self-love and Care A healthy recovery requires personal growth and self-respect. Prioritizing self-care helps people in recovery break free from negative self-talk and addictive process. The Role of Support Groups Building a Supportive Network Joining 12-step rooms, 12-step support groups, or professional addiction treatment programs provides social connection and guidance. Sharing Experiences and Strategies Participating in 12-step literature discussions or 12-step work helps a person in recovery navigate challenges and strengthen their recovery goals. Community Connections Engaging with Local Resources Addiction treatment programs and addiction counseling services, like American Addiction Centers and Gateway Foundation, provide structured support. Leveraging Online Support Platforms Online groups help individuals in recovery from substance use connect with others in similar situations. Balancing Recovery Goals with Relationships Setting Personal Boundaries Maintaining healthy people in your social circles and avoiding toxic relationships is essential for a successful relationship in recovery. Aligning Relationship Choices with Recovery Needs Surrounding oneself with people in recovery who support a solid foundation in sobriety helps prevent engagement in substance addiction or exposure to situations with drugs. Conclusion: Sustaining Sobriety through Healthy Relationships The journey to recovery can be challenging, but relationships during recovery can either strengthen or weaken an individual’s resolve. Prioritizing healthier relationships, setting personal boundaries, and engaging in addiction treatment attempts through treatment programs and addiction treatment field support long-term sobriety. Through healthy communication and meaningful relationships, individuals can sustain their path to sobriety while maintaining a life of sobriety free from addictive substance dependence. Seeking Treatment? We Can Help! At Sullivan Recovery, as an in-network provider we work with most insurance plans, such as: Tricare Blue Shield Magellan Health First Health Network The Holman Group Cigna Anthem BCBS Aetna Humana TriWest HMC Healthworks Molina UnitedHealthcare Optum UMR And More If you or a loved one are struggling with mental health challenges or substance abuse, reach out to Sullivan Recovery today. Our team of compassionate professionals is here to support your journey towards lasting well-being. Give us a call at 949-836-7180. Frequently Asked Questions 1. Why are healthy relationships important during the recovery process? Healthy relationships provide emotional stability, mutual respect, and honest communication, which are essential for maintaining sobriety. A person in recovery benefits from supportive relationships that encourage personal growth, reinforce sobriety goals, and help prevent unhealthy coping mechanisms. Having strong relationships can reduce stress and offer a safe space for navigating the challenges of addiction recovery. 2. What are the risks of engaging in romantic relationships early in recovery? Entering a romantic relationship too soon in the recovery process can be risky because early sobriety requires
Is Lexapro Addictive? Understanding the Risks and Realities

Table of Contents Seeking Drug Or Alcohol Detox? Sullivan Recovery is a leading drug and alcohol detox in Mission Viejo, California. Call Today! Clinically Reviewed By: Rachel Sweet | LMFT Is Lexapro Addictive? Understanding the Risks and Realities What is Lexapro? Lexapro (escitalopram) is a prescription drug that belongs to a class of antidepressants called selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). It is primarily used for the treatment of depression and various mental health conditions such as Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD), Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD), and Panic Disorder. By increasing serotonin levels, Lexapro helps improve emotional stability and reduce symptoms of depression and symptoms of anxiety. Mechanism of Action Lexapro works by inhibiting the reabsorption of chemical serotonin in the brain, allowing for an effective drug level that enhances therapeutic effects. This process helps regulate negative thought patterns, promote emotional stability, and improve daily life for people with depression symptoms or anxiety disorders. Conditions Treated by Lexapro Healthcare professionals commonly prescribe Lexapro for: Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) (off-label) Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD) (off-label) Panic Disorder Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) (off-label) Bipolar Disorder (as an adjunct therapy) Understanding Addiction Drug addiction is a dangerous condition that involves compulsive drug-seeking behavior despite harmful consequences. It often leads to physical dependence, psychological dependence, and long-term dependence. Addictive substances usually produce euphoric highs, making them more likely to be misused for recreational purposes. Lexapro and the Risk of Addiction Lexapro is not classified as an addictive medication, as it does not induce euphoric effects or trigger compulsive behaviors. However, long-term use may result in physical dependence, requiring a tapering schedule to avoid severe withdrawal symptoms. Signs and Symptoms of Lexapro Misuse While Lexapro has a low risk of addiction, some individuals misuse it by: Taking larger doses than prescribed Using it for recreational abuse Mixing it with illicit substances or other prescription medications Psychological Effects Emotional numbness Disturbing dreams Psychological addiction Physical Effects Gastrointestinal issues Weight gain or Weight loss Sleep disturbances Muscle stiffness Blurred vision Loss of coordination Blood sugar fluctuations Accelerated heart rate Blood pressure changes Demographics at Risk for Misuse Certain individuals face a higher risk of addiction, including: Those with a history of substance abuse Individuals with co-occurring disorders People struggling with mental health disorders Patients using prescription drug misuse for self-medication The Difference Between Addiction and Dependence Physical addiction: Occurs when the body requires the drug to function normally. Psychological dependence: Involves a mental reliance on the drug to cope with stress or mental health issues. Lexapro Abuse vs. Recreational Use Unlike opioids or benzodiazepines, Lexapro does not produce euphoric highs or immediate adverse effects when misused. However, using it outside prescribed guidelines can lead to harmful effects such as serotonin syndrome, a deadly condition caused by the excessive accumulation of serotonin in the brain. Withdrawal Symptoms and Management Stopping Lexapro suddenly can lead to Common withdrawal symptoms, also known as SSRI discontinuation syndrome. These may include: Flu-like symptoms Extreme sadness Sensory disturbances (e.g., brain zaps) Sleep disturbances Nasal passages congestion Severe withdrawal symptoms such as suicidal thoughts Managing the Withdrawal Process Tapering schedule under the guidance of a healthcare provider Alternative medications to ease withdrawal discomfort Behavioral therapies to address psychological factors Medication-assisted treatment for those experiencing intense withdrawal symptoms Treatment Options for Lexapro Misuse Medically-Supervised Detox A Drug detox program in a medical facility can help manage physical symptoms and reduce health risks associated with withdrawal. Top-tier medical Lexapro detox facilities provide a structured environment with dedicated teams for supervision. Behavioral Therapies Therapeutic interventions such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Experiential Therapy help address behavioral dependencies and promote lasting recovery. Seeking Professional Help A comprehensive approach to treatment includes: Addiction treatment programs tailored to individual needs Specialized outpatient treatment programs with flexible treatment schedules Comprehensive day-long therapy sessions 12-step group therapy to foster a supportive environment Societal Implications of Lexapro Prescribing Practices With the widespread use of antidepressant medications, concerns about long-term wellness and future dependency have grown. Healthcare professionals must ensure that patients receive effective treatment programs while minimizing negative consequences and critical consequences of prolonged use. Conclusion Lexapro is not an addictive drug, but long-term use may lead to physical dependence and withdrawal symptoms. A holistic approach to discontinuation, including alternative medications, behavioral therapies, and addiction treatment, can help ease the withdrawal process and support a life of sobriety. If you or a loved one struggles with substance abuse issues related to prescription medications, seeking help from a drug rehab center or recovery specialists is crucial for long-term recovery. Seeking Treatment? We Can Help! At Sullivan Recovery, as an in-network provider we work with most insurance plans, such as: Tricare Blue Shield Magellan Health First Health Network The Holman Group Cigna Anthem BCBS Aetna Humana TriWest HMC Healthworks Molina UnitedHealthcare Optum UMR And More If you or a loved one are struggling with mental health challenges or substance abuse, reach out to Sullivan Recovery today. Our team of compassionate professionals is here to support your journey towards lasting well-being. Give us a call at 949-836-7180. Frequently Asked Questions 1. Is Lexapro considered an addictive drug? No, Lexapro is not classified as an addictive drug because it does not produce euphoric highs or intense cravings like opioids or stimulants. However, long-term use can lead to physical dependence, meaning the body adapts to the medication and may require a tapering schedule to avoid severe withdrawal symptoms when discontinuing use. While psychological dependence can occur in some individuals, Lexapro does not lead to compulsive drug-seeking behavior commonly associated with substance abuse issues. 2. What are the withdrawal symptoms of Lexapro? Stopping Lexapro suddenly can cause common withdrawal symptoms, often referred to as SSRI discontinuation syndrome. These symptoms may include flu-like symptoms such as fatigue, nausea, and headaches, as well as sensory disturbances like brain zaps. Many individuals experience sleep disturbances, including disturbing dreams or insomnia, along with extreme sadness, irritability, and mood swings. Physical effects such as dizziness, loss of coordination,
Antihistamine Addiction: Understanding the Risks and Recovery Options

Table of Contents Seeking Drug Or Alcohol Detox? Sullivan Recovery is a leading drug and alcohol detox in Mission Viejo, California. Call Today! Clinically Reviewed By: Rachel Sweet | LMFT Antihistamine Addiction: Understanding the Risks and Recovery Options What Are Antihistamines? Antihistamines are a class of drugs used to treat allergic reactions, nasal congestion, and motion sickness. They work by blocking cholinergic receptors, reducing the effects of histamine on the body. Antihistamines are found in over-the-counter medications, cold medications, and anti-allergy medication. While these drugs provide allergy relief, they also have abuse potential due to their sedative effects and, in some cases, hallucinogenic effects. Common Types of Antihistamines Antihistamines are divided into first-generation antihistamines and second-generation antihistamines. First-generation antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine tablets and diphenhydramine cream, cause sedating effects and are often used as a sleep aid or cold remedy. These drugs also exhibit anticholinergic properties, which can contribute to cognitive impairment and drug-seeking behavior when misused. Second-generation antihistamines, such as loratadine and cetirizine, are considered non-sedating antihistamines and have a lower risk of addiction. However, they still carry a potential for misuse when taken in larger doses. Understanding Antihistamine Addiction Antihistamine misuse occurs when individuals take excessive amounts of these drugs for their euphoric effects, psychoactive effects, or Cocaine-like neurochemical effects. This can lead to psychological dependence, where a person feels compelled to use the drug even when it causes adverse effects. Some individuals develop substance use disorders, experiencing cravings for antihistamines and difficulty stopping use despite severe side effects. What Leads to Antihistamine Dependency? Several risk factors contribute to addiction to antihistamines. Individuals with a history of substance abuse or co-occurring mental health concerns may be at an elevated risk of developing a dependency. Factors such as Ease of access, self-medication for co-occurring mental health issues, and prolonged use for allergy symptoms or cold medications increase the risk of addiction. Signs and Symptoms of Addiction The symptoms of antihistamine addiction include: Secretive behavior surrounding drug use Increased daily dose beyond the usual dose Using antihistamines for non-medical purposes Social withdrawal and neglecting responsibilities Experiencing fluctuations in mood or aggressive behavior Physical symptoms such as dry nose, urinary retention, and Loss of appetite Effects of Antihistamine Misuse The effects of antihistamine addiction can be both physical and psychological. Individuals may experience common side effects such as drowsiness, chest congestion, and dizziness. More serious dangerous side effects include cognitive impairment, self-injurious behavior, and addiction-related behaviors. Long-term use can alter brain chemistry, affecting the nucleus accumbens, a key region involved in drug tolerance and addiction. Dangers of Long-Term Use Chronic diphenhydramine abuse can result in behavioral effects, including mood swings, sleep disturbances, and co-occurring mental health disorders. The effects of diphenhydramine on the brain can lead to physical dependence and difficulty functioning without the drug. Long-term use may also contribute to compounds in drug dependence, increasing the likelihood of drug overdose deaths. Withdrawal Symptoms When stopping antihistamine use, individuals may experience symptoms of Antihistamine withdrawal, including: Uncomfortable symptoms such as insomnia, anxiety, and restlessness Drug withdrawal times varying depending on the severity of dependency Physical withdrawal symptoms like nausea, dizziness, and fatigue Psychological withdrawal symptoms such as mood swings and depression Risks of Tolerance and Overdose Repeated misuse increases drug tolerance, requiring individuals to take larger doses to achieve the same sedative H1 antihistamines effects. This raises the risk of overdose, which can cause severe side effects such as respiratory distress, seizures, and cardiac complications. Treatment Options for Antihistamine Addiction Detoxification Process The detox process is the first step in recovery. Medical professionals at institutions like Baylor College of Medicine can provide structured detox plans to help manage Antihistamine withdrawal symptoms safely. Inpatient Rehabilitation Programs For individuals with severe addiction, inpatient rehab offers comprehensive care through structured treatment. Facilities in College Station, Brazos Valley, and other locations provide professional support. Behavioral Therapies Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a key component of addiction treatment, helping individuals address aspects of addiction and develop coping strategies. Behavioral therapies play a crucial role in promoting long-term recovery. Importance of Support Groups Support groups, such as Drug Court programs and National Helpline resources, offer confidential helpline support for individuals seeking recovery. The Importance of Seeking Help Resources Available in California California offers a wide range of treatment options for individuals struggling with substance abuse. The state is home to numerous rehabilitation centers, including inpatient, outpatient, and detox programs. Organizations such as the California Department of Health Care Services (DHCS) provide resources for addiction treatment. Local rehab centers offer medical and therapeutic support, helping individuals manage withdrawal symptoms and develop healthier coping strategies. Consulting a pharmacist for advice or a doctor for advice can also help individuals explore safe alternatives to antihistamine medications. For additional support, confidential helplines and peer support groups are available throughout the state. Recovery Avenues and Support Systems The recovery journey requires commitment, professional guidance, and peer support. By addressing co-occurring mental health issues, individuals can develop healthier habits and reduce reliance on counter drugs for relief. Conclusion: Moving Towards Recovery Abusers of antihistamines often struggle with physical dependence and psychological dependence, but recovery is possible. Seeking medical advice, undergoing a detoxification process, and participating in long-term recovery programs can help individuals regain control over their lives. If you or a loved one is struggling, reaching out for help is the first step toward healing. Seeking Treatment? We Can Help! At Sullivan Recovery, as an in-network provider we work with most insurance plans, such as: Tricare Blue Shield Magellan Health First Health Network The Holman Group Cigna Anthem BCBS Aetna Humana TriWest HMC Healthworks Molina UnitedHealthcare Optum UMR And More If you or a loved one are struggling with mental health challenges or substance abuse, reach out to Sullivan Recovery today. Our team of compassionate professionals is here to support your journey towards lasting well-being. Give us a call at 949-836-7180. Frequently Asked Questions 1. Can you become addicted to antihistamines? Yes, antihistamines, especially first-generation antihistamines like diphenhydramine (Benadryl), have a potential for misuse due to their
Inspirational Depression Quotes: Finding Strength Through Words

Table of Contents Seeking Drug Or Alcohol Detox? Sullivan Recovery is a leading drug and alcohol detox in Mission Viejo, California. Call Today! Clinically Reviewed By: Rachel Sweet | LMFT Inspirational Depression Quotes: Finding Strength Through Words Understanding Depression Depression is a complex mental health condition that affects millions of American adults. It can feel like an all-consuming challenge, making normal life seem impossible. People with depression often struggle with depressive episodes that bring emotional pain, mental pain, and even physical pain. Mental health disorders, including major depression and bipolar disorder, can create severe depression that impacts daily routine. Famous author Sylvia Plath once wrote, “I am afraid of getting older. I am afraid of getting married. Spare me from cooking three meals a day. Spare me from the relentless cage of routine and rote.” This quote resonates with those experiencing a mental health struggle, as depression can make even the simplest tasks feel overwhelming. The Power of Words Words can shape our thoughts, offering positive vibes during dark times. An inspirational quote can serve as an antidote for anxiety and provide a beautiful reminder that depression is not a life sentence. Writers like John Green and Matt Haig have used their experiences with mental health challenges to inspire others through words. How Quotes Can Inspire Hope A gentle reminder through depression quotes can shift a person’s outlook on life. When someone is in the middle of winter emotionally, reading an inspiring quote can help them find an invincible summer within themselves, a reference to the famous Albert Camus quote: “In the depth of winter, I finally learned that within me there lay an invincible summer.” The Role of Quotes in Recovery Mental health quotes are powerful reminders that Tough times do not last forever. Many celebrities have spoken about their mental health journey, showing that even the strongest people have faced mental health issues. Inspirational Quotes on Depression Quotes from Famous Authors “Not everything that is faced can be changed, but nothing can be changed until it is faced.” – James Baldwin “There is some good in this world, and it’s worth fighting for.” – J.R.R. Tolkien “Hardships often prepare ordinary people for an extraordinary destiny.” – C.S. Lewis Quotes from Celebrities “You are not alone, and you are not broken.” – Kristen Bell “I was drowning, and nobody saw my struggle.” – Demi Lovato “I have the same fears, the same depression, the same anxiety of life.” – Lady Gaga Therapeutic Benefits of Motivational Quotes Coping Mechanisms through Words Repeating a positive depression quote can help people with depression combat negative thinking. Authors like Jasmine Warga and Nina LaCour have written about the impact of depressive episodes and how words can serve as a natural mood booster. Emotional Resilience and Affirmations Daily affirmation quotes from inspiring figures like Michelle Obama, Maya Angelou, and Stephen Fry can remind people that mental health issues do not define them. A favorite depression quote can serve as a direct route to emotional healing. Self-Care and Mindfulness Practicing deep breathing techniques and conscious breathing while reading an inspirational quote can create a sense of calm. Thich Nhat Hanh emphasized the importance of mindfulness in mental health, stating that “Feelings come and go like clouds in a windy sky. Conscious breathing is my anchor.” Integrating Quotes into Daily Life Practicing Mindfulness with Inspirational Quotes Including mental health quotes in a daily routine can help shift perspectives. Whether it’s reading a quote from Anne Hathaway or reflecting on words from Winston Churchill, these powerful reminders can provide comfort in difficult times. Sharing Personal Stories Many people who have faced manic depression or chronic depression find strength in sharing their stories. Writers like Andrew Solomon and Barbara Kingsolver have explored the experience of depression, helping others feel seen. Testimonials of Hope Actors like Keanu Reeves and Lili Reinhart have shared their mental health challenges, proving that even in the darkest moments, healing is possible. As Nido Qubein once said, “Your present circumstances don’t determine where you go; they merely determine where you start.” Overcoming Challenges with Words A beautiful reminder from Carrie Fisher is: “Stay afraid, but do it anyway. What’s important is the action.” This favorite quote reinforces the idea that mental health struggles can be managed with courage. The Importance of Seeking Help Mental Health Treatment Options Depressed people should never feel like they have to manage mental health disorders alone. Mental health professionals can provide guidance for those facing a depressed mood, major depression, or mood disorders. When to Seek Professional Help If someone is experiencing a persistent bad mood, memories depression, or physical symptoms like exhaustion, it may be time to seek help. A business asset like a therapist can help address negative thinking and provide strategies for healing. As Dwayne Johnson once said, “Tough times don’t last, tough people do.” Final Thoughts Mental health conditions are part of the human experience, but they do not define a person. Depression symptoms may feel overwhelming, but embracing health through mental health treatment and support can bring hope. Whether it’s a favorite quote from Bob Marley or a simple daily affirmation, words have the power to heal. As Charlie Chaplin once said, “A day without laughter is a day wasted.” Even in dark times, there is always light ahead. Seek support, embrace positive depression quotes, and remember—this is just one chapter in a much larger story. Seeking Treatment? We Can Help! At Sullivan Recovery, as an in-network provider we work with most insurance plans, such as: Tricare Blue Shield Magellan Health First Health Network The Holman Group Cigna Anthem BCBS Aetna Humana TriWest HMC Healthworks Molina UnitedHealthcare Optum UMR And More If you or a loved one are struggling with mental health challenges or substance abuse, reach out to Sullivan Recovery today. Our team of compassionate professionals is here to support your journey towards lasting well-being. Give us a call at 949-836-7180. Frequently Asked Questions 1. How can inspirational depression quotes help with mental health challenges? Inspirational
What Is Narcan? A Guide to Naloxone and Opioid Overdose Reversal
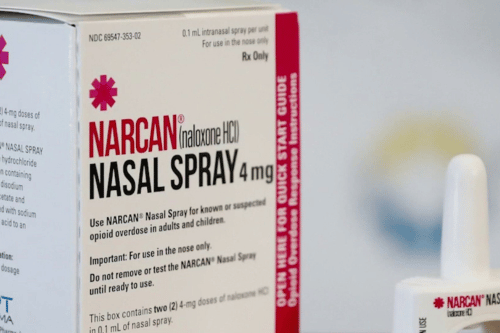
Table of Contents Seeking Drug Or Alcohol Detox? Sullivan Recovery is a leading drug and alcohol detox in Mission Viejo, California. Call Today! Clinically Reviewed By: Rachel Sweet | LMFT What Is Narcan? A Guide to Naloxone and Opioid Overdose Reversal What Is Narcan (Naloxone)? Narcan is a life-saving medication used to reverse opioid overdoses. It works by blocking opioid receptors in the brain, quickly restoring normal breathing in an opioid emergency. The active ingredient, naloxone hydrochloride nasal spray, is available in multiple forms of naloxone, including Narcan nasal spray, an injectable form, and an ampoule of naloxone used by medical professionals. The effects typically last 30-90 minutes, making it essential to seek medical care after use. Understanding Opioid Overdoses An opioid overdose occurs when a person takes too much of an opioid drug, leading to dangerous suppression of the central nervous system. Synthetic opioids, such as fentanyl, increase the likelihood of fatal overdoses, contributing to the current overdose crisis. According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, overdoses from prescription opioids and illegal opioids have led to a dramatic rise in overdose deaths. Signs of an Opioid Overdose Recognizing the signs of opioid overdose is critical for timely intervention. A person experiencing an overdose may have shallow breathing, clammy skin, a rapid heart rate, or abnormal heart rhythms. Other warning signs include gurgling sounds, confusion, and a bluish colour of skin. If left untreated, an overdose can lead to brain damage and death. If someone appears to be experiencing an overdose, immediate administration of naloxone nasal spray products can save their life. How Narcan Works As an opioid antagonist, Narcan quickly blocks opioids from attaching to δ-opioid receptors and κ-opioid receptors, reversing the effects of opioid overdose. Within symptoms within minutes, breathing can improve, and the person may regain consciousness. However, because Narcan only lasts 20-90 minutes, the risk of an overdose after naloxone wears off is high, particularly for those exposed to high-dose opioid medications or potent opioids like fentanyl. Administration of Narcan Narcan is available in two main forms: naloxone nasal spray and injectable naloxone. The nasal spray is the most common and easy-to-use form of naloxone, designed for emergency situations where medical professionals may not be immediately available. The injectable form requires intramuscular or subcutaneous injection and is often used in emergency room settings. To administer Narcan, check for signs of overdose, such as breathing in people overdosing slowing or stopping. If the person is unresponsive, use the nasal spray by inserting it into one nostril and pressing the plunger. If using an injectable form, administer the naloxone dose into the thigh or upper arm. Afterward, call 911 and provide rescue breathing if necessary. Since the effects of naloxone products wear off within 30-90 minutes, additional doses of naloxone may be required. Who Should Carry Narcan? People at risk for opioid overdose, including those using high-dose opioid medications, should have take-home naloxone available. Friends, family members, and caregivers of opioid users should also carry naloxone kits in case of emergencies. First responders, medical technicians, and members of community-based opioid overdose prevention programs play a crucial role in increasing access to naloxone in high-risk populations. Many health departments and pharmacies offer naloxone from community distribution programs to improve public health outcomes. Importance of Narcan Accessibility The retail cost of Narcan varies based on the brand of naloxone and the individual’s insurance benefit. Many patients with insurance should check their insurance company for coverage, while patients without insurance can access cost assistance programs through healthcare providers or harm reduction programs. Some states allow naloxone from pharmacies to be purchased without a prescription, and community-based naloxone programs distribute communal naloxone for free. Effectiveness of Narcan Narcan is highly effective, reversing opioid overdoses in over 90% of cases. However, due to the increasing presence of synthetic opioids, multiple doses of naloxone may be required. In some cases, potent opioid exposure can cause an overdose after naloxone wears off, requiring ongoing medical treatment. Potential Side Effects While generally safe, effects from naloxone can trigger opioid withdrawal symptoms, including stomach pain, nausea, and vomiting. Other adverse effects may include rapid heart rate, dizziness, sweating, and headache. In some cases, blood pressure confusion and blood pressure fluid accumulation may occur. Individuals with opioid dependence may experience a bad reaction, becoming agitated or disoriented after administration. Co-Prescribing Naloxone with Opioids To reduce overdose risks, doctors often include the prescription of naloxone when prescribing opioid drugs, particularly for chronic pain patients or those taking concomitant opioids. This practice, known as Co-Prescribing Naloxone, is encouraged by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Training Resources for Narcan Use Various organizations, including health departments, harm reduction centers, and the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, offer free training on administration of naloxone can help save lives. Programs such as Alberta Health Services, Health Canada, and the Center for Harm Reduction Services provide education on overdose prevention and access to naloxone products. Legal Considerations Most states have Good Samaritan laws that protect individuals who administer Narcan in an emergency. Additionally, distribution of naloxone is supported through community-based opioid overdose prevention programs, increasing access to naloxone in high-risk areas. Final Thoughts Narcan is an essential tool in reducing overdose death and improving public health. Expanding access to naloxone through communal settings and harm reduction initiatives can help address the burden of prescription opioid overdoses. If you or someone you know is at risk, carrying Narcan could be the difference between life and death. Seeking Treatment? We Can Help! At Sullivan Recovery, as an in-network provider we work with most insurance plans, such as: Tricare Blue Shield Magellan Health First Health Network The Holman Group Cigna Anthem BCBS Aetna Humana TriWest HMC Healthworks Molina UnitedHealthcare Optum UMR And More If you or a loved one are struggling with mental health challenges or substance abuse, reach out to Sullivan Recovery today. Our team of compassionate professionals is here to support your journey towards lasting well-being. Give us a call at 949-836-7180. Frequently Asked
HHC vs THC: Understanding the Differences

Table of Contents Seeking Drug Or Alcohol Detox? Sullivan Recovery is a leading drug and alcohol detox in Mission Viejo, California. Call Today! Clinically Reviewed By: Rachel Sweet | LMFT HHC vs THC: Understanding the Differences Cannabis-derived compounds like THC and HHC offer unique psychoactive effects and therapeutic benefits. While both come from the cannabis plant, their chemical structure and pharmacological activity differ. Understanding their effects, legal status, and potential benefits can help users make informed choices in the cannabis marketplace. Overview of THC Chemical Composition and Structure THC, or delta-9 THC, is one of the most abundant cannabinoids found in the cannabis sativa plant. Its molecular structure contains a ninth carbon atom, which allows it to bind effectively to CB1 cannabinoid receptors in the brain, producing a euphoric feeling. This interaction with endocannabinoid receptors triggers various psychoactive properties and therapeutic potential. Effects on the Body and Mind As a psychoactive compound, Delta 9 affects mood, perception, and cognition. It can induce euphoric feelings, relaxation, and appetite stimulation. However, it also has common side effects, including dry mouth, dizziness, increased heart rate, and undesired side effects like paranoia in higher doses. Common Uses and Therapeutic Benefits THC products are widely used for pain relief, chronic pain management, and as part of drug treatment programs. Medical professionals often recommend THC for appetite stimulation, nausea reduction, and its therapeutic properties in treating anxiety and insomnia. Legal Restrictions THC faces strict legal restrictions in many regions. It is federally illegal in the U.S. but permitted for medical and recreational use in some states. The cannabis industry continues to advocate for broader legalization due to the beneficial effects of THC in healthcare. Overview of HHC Discovery and Chemical Process HHC (Hexahydrocannabinol) was first discovered by Roger Adams in the 1940s when he added hydrogen atoms to delta-9 THC in a process called hydrogenation. This modification changes its molecular formula, making it more stable with a longer shelf life compared to THC. Therapeutic Potential and Effects HHC is a natural cannabinoid found in small amounts in the cannabis plant, but most HHC products are synthesized from hemp-derived CBD. Users report milder effects than THC, with potential benefits such as pain relief, stress reduction, and mild psychoactive properties. However, research on long-term health effects is still limited. Legal Status and Product Availability HHC exists in a legal gray area since it is derived from hemp plants rather than marijuana. It is often sold in states where THC products are restricted. However, some states have begun regulating or banning hemp-derived cannabinoids, including Delta-8 Products and Delta-10 Products. Comparison of HHC and THC Psychoactive Potency THC is highly psychoactive, producing stronger effects due to its direct binding to CB1 receptors. HHC has weaker CB1 cannabinoid receptor signaling, resulting in milder effects and fewer adverse effects like paranoia or anxiety. Therapeutic Potential and User Experiences Both cannabinoids offer therapeutic benefits, but THC is better studied and widely used for chronic pain and nausea. HHC may appeal to those seeking benefits of cannabinoids without intense psychoactive effects. User preferences vary—some favor THC for its stronger effects, while others choose HHC for its gentler impact and reduced risk of undesired side effects. Health and Safety Considerations Side Effects of THC THC can cause dry mouth, dizziness, increased heart rate, and psychoactive effects such as paranoia. High doses may intensify these potential side effects. Side Effects of HHC HHC has similar but milder effects, including dry mouth, slight dizziness, and potential nausea. As a synthetic cannabinoid, concerns exist about heavy metals or contaminants in poorly regulated cannabis products. Safety Profiles of Both Cannabinoids Both compounds interact with cannabinoid receptor CB1, but HHC’s complex after CB1R stimulation results in milder effects. While THC has been extensively studied, research on (9R)-HHC administration and long-term health effects is still developing. Choosing the Right Cannabinoid for You Individual Health Goals and Personal Preferences If you need strong pain relief, Delta 9 THC may be more effective. If you prefer milder effects with fewer adverse effects, HHC could be a better alternative. Recommended Usage Guidelines Start with a low dose and increase gradually. Medical professionals advise checking legal restrictions and product quality before using Hemp and Cannabis Products. Frequently Asked Questions Do HHC and THC Show Up on Drug Tests? Yes. Standard drug tests screen for delta-9 THC metabolites, and HHC products may trigger similar results due to their interaction with cannabinoid receptors. What Are the Legal Standings of HHC and THC in Different States? THC is federally illegal but allowed in some states. HHC’s legal status depends on state regulations regarding hemp-derived products. How Are HHC Products Made Compared to THC Products? HHC is synthesized from hemp-derived CBD through hydrogenation, which modifies its chemical compounds. THC is extracted from the sativa plant or produced as a synthetic cannabinoid. Can HHC and THC Be Used Together? Yes, some users mix them to balance psychoactive properties and therapeutic benefits, but combining them may increase potential side effects. Final Thoughts Both THC and HHC have unique therapeutic potential and applications. Your choice depends on individual health goals, legal restrictions, and tolerance for psychoactive effects. Always consult a professional before using hemp-derived cannabinoids or exotic cannabinoids in the evolving cannabis industry. Seeking Treatment? We Can Help! At Sullivan Recovery, as an in-network provider we work with most insurance plans, such as: Tricare Blue Shield Magellan Health First Health Network The Holman Group Cigna Anthem BCBS Aetna Humana TriWest HMC Healthworks Molina UnitedHealthcare Optum UMR And More If you or a loved one are struggling with mental health challenges or substance abuse, reach out to Sullivan Recovery today. Our team of compassionate professionals is here to support your journey towards lasting well-being. Give us a call at 949-836-7180. Frequently Asked Questions 1. Do HHC and THC Have the Same Psychoactive Effects? HHC and THC both interact with CB1 cannabinoid receptors, but their psychoactive properties differ. Delta-9 THC is known for its strong euphoric feeling, while HHC produces milder effects. THC binds directly to cannabinoid
